alb3805219
Physical Basis of Heredity, T.H. Morgan, 1919
|
Zu einem anderen Lightbox hinzufügen |
|
Zu einem anderen Lightbox hinzufügen |



Haben Sie bereits ein Konto? Anmelden
Sie haben kein Konto? Registrieren
Dieses Bild kaufen

Titel:
Physical Basis of Heredity, T.H. Morgan, 1919
Untertitel:
Siehe automatische Übersetzung
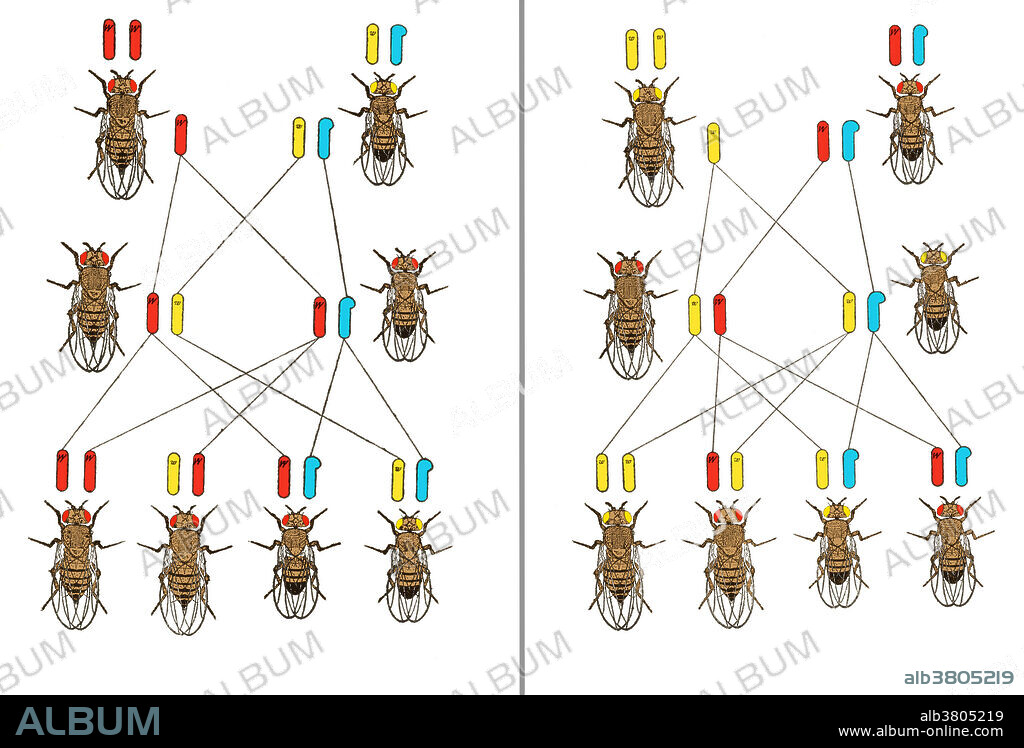
Cross between white-eyed male and red-eyed female of the vinegar fly. From The physical basis of heredity by Thomas Hunt Morgan, 1919. Thomas Hunt Morgan (1866-1945) was the recipient of the 1933 Nobel Prize in Medicine for his discoveries of the role played by chromosomes in heredity. Morgan received his Ph.D. in 1890 at Johns Hopkins University. The work that received the prize was completed over a 17-year period at Columbia University by Morgan and his students, commencing in 1910 with his discovery of the white-eyed mutation in the fruit fly, Drosophila. This led to the discovery of sex-linked inheritance, allowing chromosomes to be identified as the carriers of the hereditary material.
Persönlichkeiten:
Bildnachweis:
Album / Science Source
Freigaben (Releases):
Model: Nein - Eigentum: Nein
Rechtefragen?
Rechtefragen?
Bildgröße:
5088 x 3455 px | 50.3 MB
Druckgröße:
43.1 x 29.3 cm | 17.0 x 11.5 in (300 dpi)
 Pinterest
Pinterest Twitter
Twitter Facebook
Facebook Link kopieren
Link kopieren Email
Email
