alb3812434
Hooke's Law, Principle of Physics, 1678
|
Zu einem anderen Lightbox hinzufügen |
|
Zu einem anderen Lightbox hinzufügen |



Haben Sie bereits ein Konto? Anmelden
Sie haben kein Konto? Registrieren
Dieses Bild kaufen

Titel:
Hooke's Law, Principle of Physics, 1678
Untertitel:
Siehe automatische Übersetzung
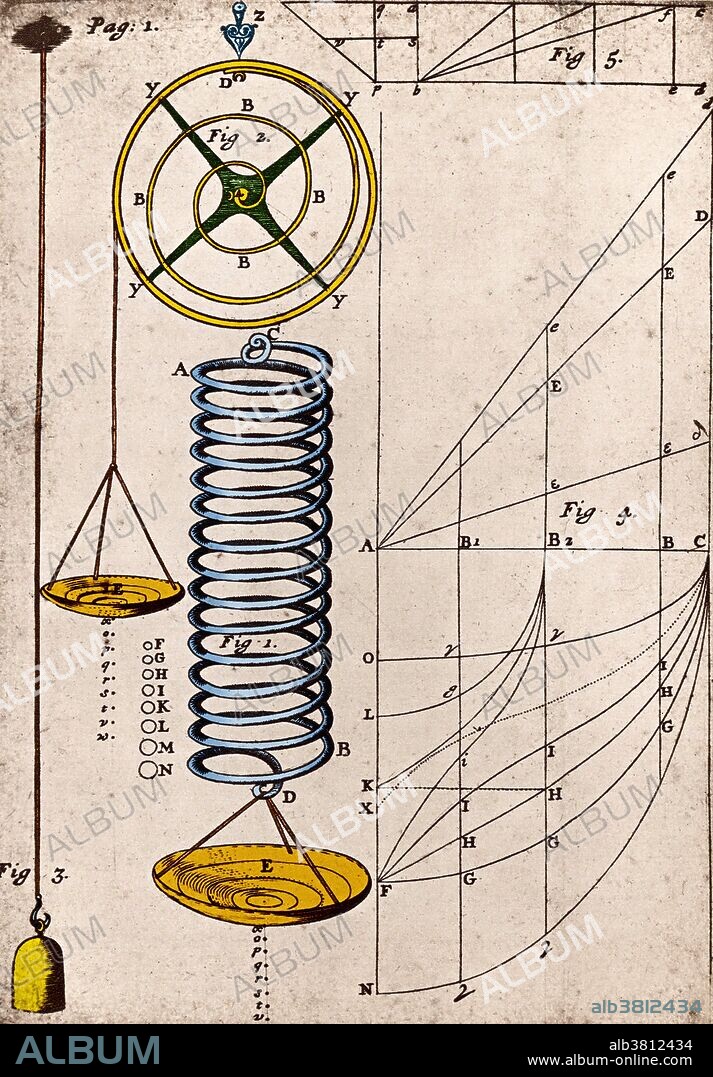
Hooke's Law, Principle of Physics, 1678. Hooke's law is a principle of physics that states that the force F needed to extend or compress a spring by some distance X is proportional to that distance. That is: F = kX, where k is a constant factor characteristic of the spring: its stiffness, and X is small compared to the total possible deformation of the spring. The law is named after 17th century English physicist Robert Hooke. He first stated the law in 1660 as a Latin anagram. He published the solution of his anagram in 1678 as: ut tensio, sic vis ("as the extension, so the force" or "the extension is proportional to the force").
Bildnachweis:
Album / Science Source
Freigaben (Releases):
Model: Nein - Eigentum: Nein
Rechtefragen?
Rechtefragen?
Bildgröße:
2406 x 3455 px | 23.8 MB
Druckgröße:
20.4 x 29.3 cm | 8.0 x 11.5 in (300 dpi)
Schlüsselwörter:
 Pinterest
Pinterest Twitter
Twitter Facebook
Facebook Link kopieren
Link kopieren Email
Email
