alb3784591
kidney stones
|
Add to another lightbox |
|
Add to another lightbox |



Title:
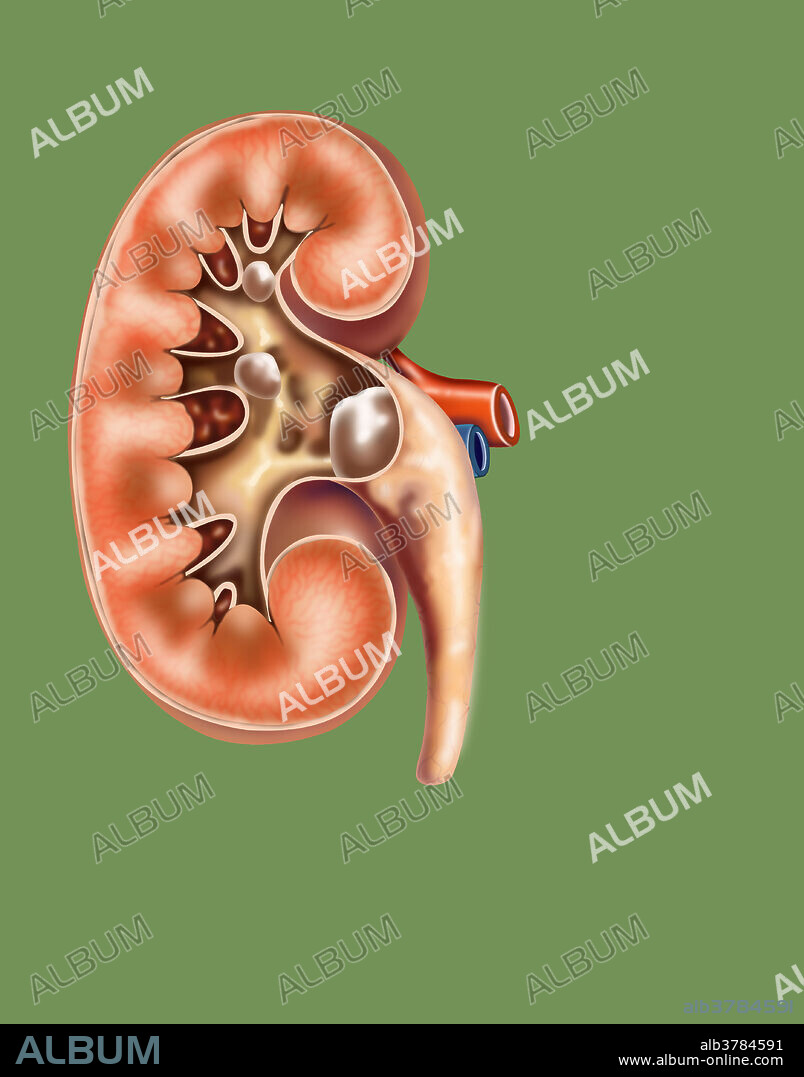
kidney stones
Caption:
A kidney stone, also known as a renal calculus is a solid concretion or crystal aggregation formed in the kidneys from dietary minerals in the urine. Urinary stones are typically classified by their location in the kidney (nephrolithiasis), ureter (ureterolithiasis), or bladder (cystolithiasis), or by their chemical composition (calcium-containing, struvite, uric acid, or other compounds). Kidney stones typically leave the body by passage in the urine stream, and many stones are formed and passed without causing symptoms. If stones grow to sufficient size they can cause obstruction of the ureter. Ureteral obstruction causes postrenal azotaemia and hydronephrosis (distension and dilation of the renal pelvis and calyces), as well as spasm of the ureter. This leads to pain, most commonly felt in the flank (the area between the ribs and hip), lower abdomen and groin (a condition called renal colic).When a stone causes no symptoms, watchful waiting is a
Personalities:
Credit:
Album / Science Source / Gwen Shockey
Releases:
Model: No - Property: No
Rights questions?
Rights questions?
Image size:
3742 x 4763 px | 51.0 MB
Print size:
31.7 x 40.3 cm | 12.5 x 15.9 in (300 dpi)
Keywords:
ABNORMAL • ANATOMICAL • ANATOMY • ART • ARTERIA • ARTERY • ARTWORK • BODY • CALCIUM • CALCULI • CALYCES • CONDITION • CORTEX • CROSS CUT • CROSS • CROSS-CUT • CROSS-SECTION • DISEASE • DISORDER • DISSECTED • DRAWING • EXCRETION • EXCRETORY • GRAPHIC • GROSS ANATOMY • HIPBONES • HORN • HUMAN • HUMANE • ILLUSTRATION • ILLUSTRATIONS • INDIVIDUAL • INTERNAL • KIDNEY • LITHIASIS • MASS • MEDICAL • MEDICINAL • MINERALS • NEPHROLITHIASIS • ORGAN • PAPILLAE • PART • PELVES • PELVIS • PERSON • PYRAMIDS • RENAL • RIGHT • ROCK • ROCKY • SALTS • SECTION • SECTIONAL • STAG • STAGHORN • STONE • STONES • STRUCTURE • SYSTEM • UNHEALTHY • URETER • URETHER • URINARY DUCT • URINARY • VEIN • VENA
 Pinterest
Pinterest Twitter
Twitter Facebook
Facebook Copy link
Copy link Email
Email

