alb10705073
Mitosis, light micrograph
|
Add to another lightbox |
|
Add to another lightbox |



Title:
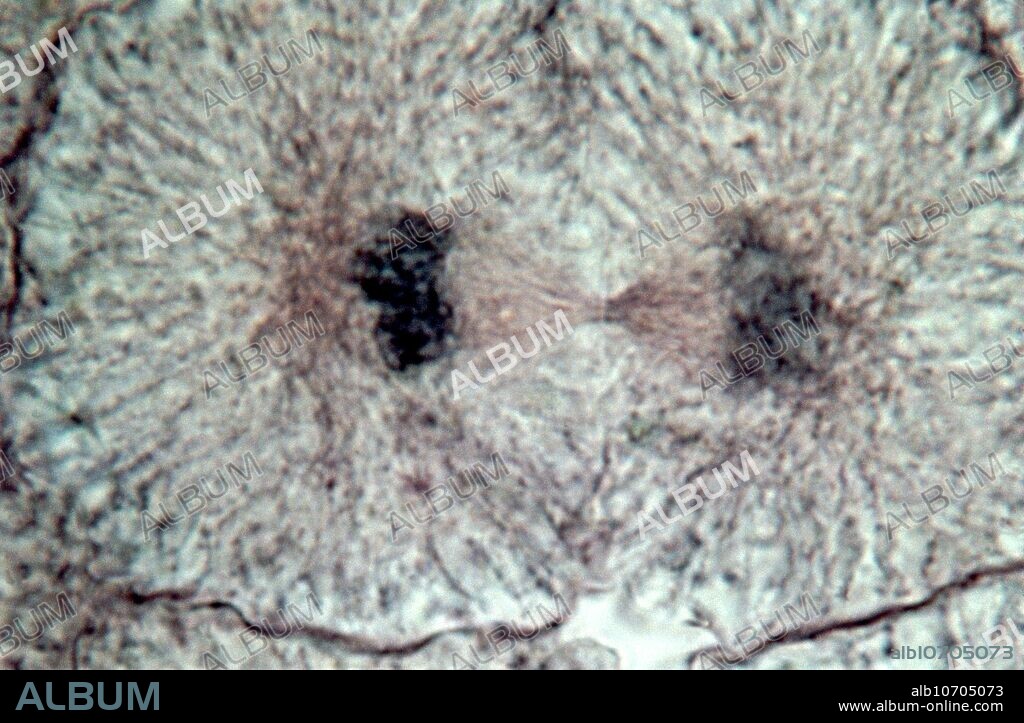
Mitosis, light micrograph
Caption:
Mitosis. Light micrograph of a whitefish cell in telophase, the last stage of mitosis (nuclear division) before cytokinesis (cell division). Mitosis is the formation of two daughter nuclei from one parent nucleus. The chromosomes have been split into their sister chromatids and moved to separate poles of the cell by microtubules (brown). Chromatids consist of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA, black). Microtubules are protein filaments that form spindles, which attach to the chromosomes and pull the sister chromatids to opposite poles of the cell. A nuclear envelope will reform around each nucleus before the cell goes on to divide in half, with each new cell retaining a copy of the parent cell's genetic information.
Credit:
Album / Science Source / BIOPHOTO ASSOCIATES
Releases:
Model: No - Property: No
Rights questions?
Rights questions?
Image size:
3655 x 2392 px | 25.0 MB
Print size:
30.9 x 20.3 cm | 12.2 x 8.0 in (300 dpi)
Keywords:
ACID • ANIMAL • BIOLOGICAL • BIOLOGY • CELL • CENTROSOME • CENTROSOMES • CHROMATID • CHROMATIDS • CHROMATIN • CHROMOSOME • CHROMOSOMES • CORE • CYTOLOGICAL • CYTOLOGY • CYTOSKELETAL • CYTOSKELETON • DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC • DIVIDING • DIVISION • DNA • GENETIC • GENETICS • KARYOKINESIS • LIGHT • LM • MICROGRAPH • MICROSCOPE • MICROTUBULE • MICROTUBULES • MITOSIS • MITOTIC • NUCLEAR • NUCLEUS • PÔLES • SCIENCE: MICROSCOPE • SEGREGATING • SEGREGATION • SEPARATING • SEPARATION • TELOPHASE • WHITEFISH
 Pinterest
Pinterest Twitter
Twitter Facebook
Facebook Copy link
Copy link Email
Email

