alb3810394
Bowman's Membrane, Retinal Layers, 1842
|
Add to another lightbox |
|
Add to another lightbox |



Title:
Bowman's Membrane, Retinal Layers, 1842
Caption:
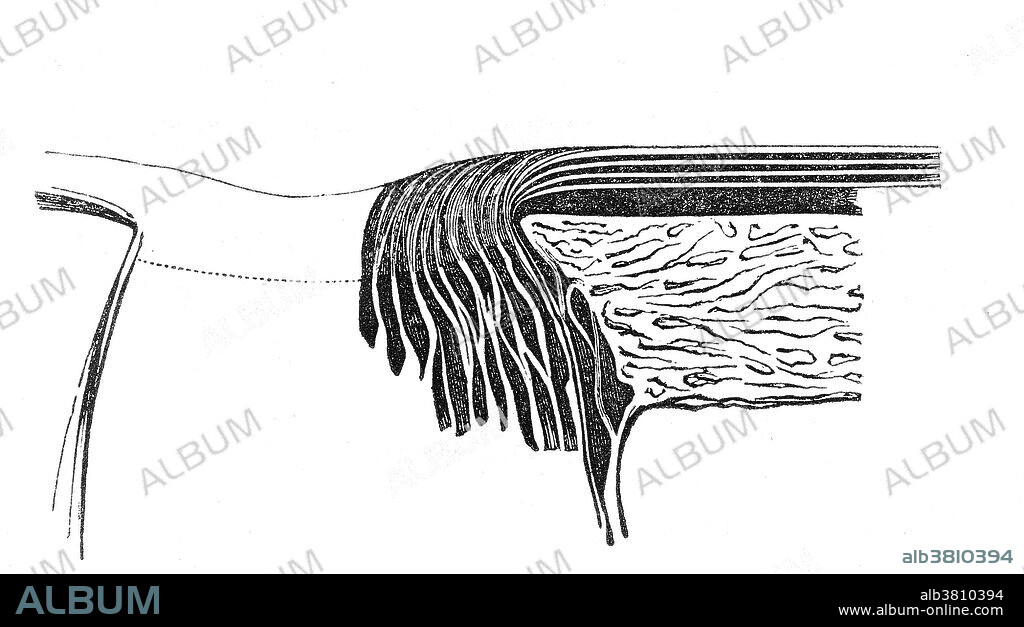
Section of the coats of the human eye at the entrance of the optic nerve to show mode of origin of layers of the retina. From "Operations of the eye," by W. Bowman, 1849. The Bowman's membrane (Bowman's layer, anterior limiting lamina, anterior elastic lamina) is a smooth, acellular, nonregenerating layer, located between the superficial epithelium and the stroma in the cornea of the eye. It is composed of strong, randomly oriented collagen fibrils in which the smooth anterior surface faces the epithelial basement membrane and the posterior surface merges with the collagen lamellae of the corneal stroma proper. In adult humans, Bowman's membrane is 8-12 ?m thick. With aging, this layer becomes thinner. The Bowman's layer, in mammals, is found only in primates. It is named after Sir William Bowman (1816-1892), an English physician, anatomist and ophthalmologist, who discovered this membrane.
Credit:
Album / Science Source / Wellcome Images
Releases:
Model: No - Property: No
Rights questions?
Rights questions?
Image size:
4050 x 2270 px | 26.3 MB
Print size:
34.3 x 19.2 cm | 13.5 x 7.6 in (300 dpi)
Keywords:
1800S • 19TH CENTURY • ANATOMICAL • ANATOMY • ART • ARTWORK • BOWMAN'S MEMBRANE • BOWMAN • COATING • COLLAGEN • CORNEA • CORNEAL • DRAWING • EYE • EYEBALL • EYEBALLS • EYES • FIBRILS • GROSS ANATOMY • HISTORIC • HISTORICAL • HISTORY • HUMAN • HUMANE • ILLUSTRATION • INDIVIDUAL • LAYERED • LAYERS • MEDICAL ILLUSTRATION • MEMBRANE • OPTIC NERVE • OPTICAL NERVE • PERSON • RETINA • RETINAE • RETINAL • RETINAS • SIGHT • STROMA • STRUCTURE • SUPERFICIAL EPITHELIUM • VISION • WILLIAM BOWMAN
 Pinterest
Pinterest Twitter
Twitter Facebook
Facebook Copy link
Copy link Email
Email

