alb3812686
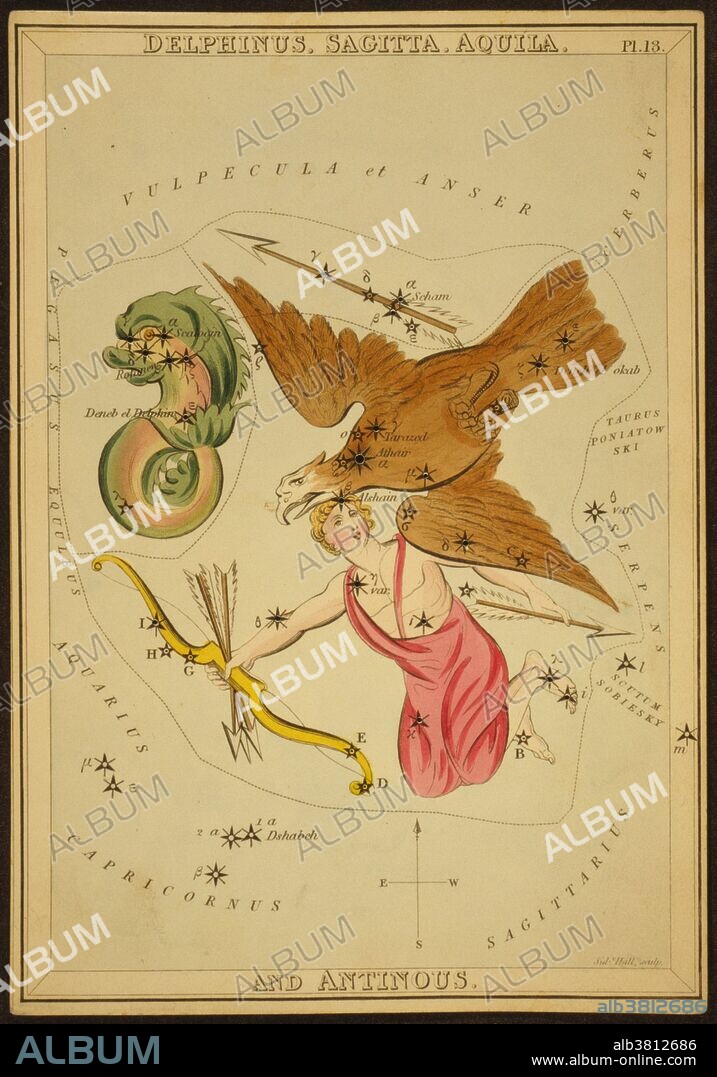
Delphinus, Sagitta and Aquila Constellations, 1825
|
Add to another lightbox |
|
Add to another lightbox |



Title:
Delphinus, Sagitta and Aquila Constellations, 1825
Caption:
Astronomical chart showing Antinous with bow and arrows, an eagle, and a dolphin forming the constellations. Delphinus is a constellation in the northern sky, close to the celestial equator. Its name is Latin for dolphin. Sagitta is Latin for arrow, and it should not be confused with the larger constellation Sagittarius, the archer. Although Sagitta is an ancient constellation, it has no star brighter than 3rd magnitude. Aquila constellation, its name is Latin for eagle and it represents the bird who carried Zeus/Jupiter's thunderbolts in Greco-Roman mythology. Aquila lies just a few degrees North of the celestial equator. It is one of the smaller constellations, ranked 69th in size. They were three of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and they remain among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. Antinous is an obsolete constellation no longer in use by astronomers, having been merged into Aquila, which it bordered to the North. Urania's Mirror is a boxed set of 32 constellation cards first published by Samuel Leigh of the Strand, London, in or shortly before 1825. An unidentified lady, referred to by her nom-de-plume, Jehoshaphat Aspin, designed these whimsical astronomy cards. The engraver was Sidney Hall.
Credit:
Album / LOC/Science Source
Releases:
Model: No - Property: No
Rights questions?
Rights questions?
Image size:
2700 x 3857 px | 29.8 MB
Print size:
22.9 x 32.7 cm | 9.0 x 12.9 in (300 dpi)
Keywords:
1825 • 19TH CENTURY • ANTINOUS • AQUILA • ARROW, THE • ART • ARTWORK • ASPIN • ASTERISM • ASTRONOMICAL • ASTRONOMY CARD • ASTRONOMY • CELEBRITY • CELESTIAL BODY • CELESTIAL SPHERE • CELESTIAL • CONSTELLATION CARD • CONSTELLATION • DELPHINUS • DOLPHIN, THE • DRAWING • EAGLE, THE • ENGRAVING • FAMOUS • HEAVENLY BODY • HEAVENLY • HISTORIC • HISTORICAL • HISTORY • ILLUSTRATION • IMPORTANT • JEHOSHAPHAT ASPIN • NOTABLE • PATTERN OF STARS • SAGITTA • SCIENCE • SIDNEY HALL • STAR CHART • STAR MAP • URANIA'S MIRROR • WELL-KNOWN
 Pinterest
Pinterest Twitter
Twitter Facebook
Facebook Copy link
Copy link Email
Email
