alb3820919
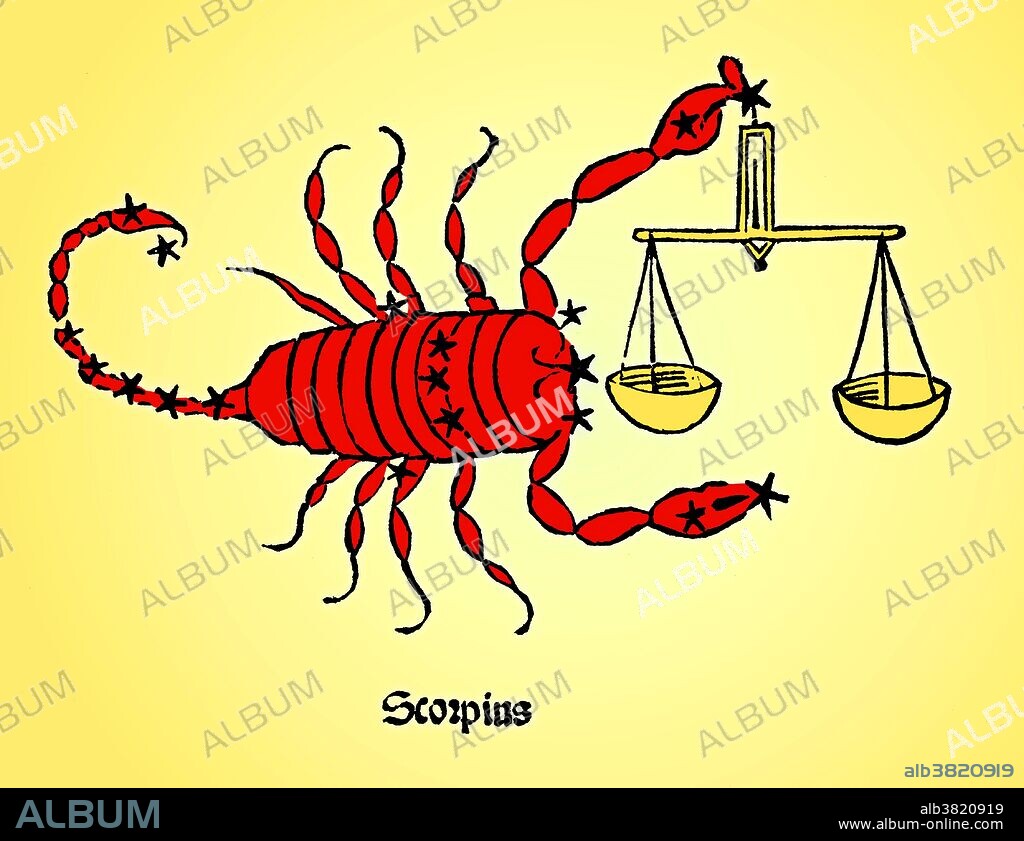
Scorpius Constellation, Zodiac, 1482
|
Añadir a otro lightbox |
|
Añadir a otro lightbox |



¿Ya tienes cuenta? Iniciar sesión
¿No tienes cuenta? Regístrate
Compra esta imagen

Título:
Scorpius Constellation, Zodiac, 1482
Descripción:
Traducción automática: Scorpius, a veces conocido como Escorpio, es una de las constelaciones del zodíaco. Su nombre en latín significa escorpión. Es una de las 48 constelaciones descritas por el astrónomo Ptolomeo del siglo II, y sigue siendo una de las 88 constelaciones modernas definidas por la Unión Astronómica Internacional. Escorpio es el octavo signo astrológico del Zodíaco, vinculado a la constelación de Escorpio. Abarca el grado 210-240 del zodíaco, un área por la que el Sol transita en promedio entre el 23 de octubre y el 22 de noviembre de cada año. Poeticon astronomicon es un atlas estelar cuya autoría está en disputa. La obra se atribuyó originalmente al historiador romano Gaius Julius Hyginus (64 a. C. - 17 d. C.). El libro enumera la mayoría de las constelaciones en el mismo orden que el Almagesto de Ptolomeo (siglo II dC), lo que ha llevado a muchos a creer que un Hyginus más reciente creó el texto. El astronomicón de Poéticon no se publicó formalmente hasta 1482, por Erhard Ratdolt. Encargó una serie de grabados en madera, pero las posiciones relativas de las estrellas se parecen poco a las descripciones dadas por Hyginus en el texto o las posiciones reales de las estrellas en el cielo.
Scorpius, sometimes known as Scorpio, is one of the constellations of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for scorpion. It is one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. Scorpio is the eighth astrological sign in the Zodiac, linked to the constellation of Scorpius. It spans the 210-240th degree of the zodiac, an area which the Sun transits on average between October 23 and November 22 each year. Poeticon astronomicon is a star atlas whose authorship is disputed. The work was originally attributed to the Roman historian Gaius Julius Hyginus (64 BC - AD 17). The book lists most of the constellations in the same order as Ptolemy's Almagest (2nd century AD) which has led many to believe that a more recent Hyginus created the text. The Poeticon astronomicon was not formally published until 1482, by Erhard Ratdolt. He commissioned a series of woodcuts, but the relative positions of the stars bear little resemblance to the descriptions given by Hyginus in the text or the actual positions of the stars in the sky.
Crédito:
Album / Science Source
Autorizaciones:
Modelo: No - Propiedad: No
¿Preguntas relacionadas con los derechos?
¿Preguntas relacionadas con los derechos?
Tamaño imagen:
4500 x 3462 px | 44.6 MB
Tamaño impresión:
38.1 x 29.3 cm | 15.0 x 11.5 in (300 dpi)
Palabras clave:
ARTE • ASTROLOGIA • ASTROLOGICO • ASTRONOMIA • ASTRONÓMICO • CELESTE • CELESTIAL SPHERE • CELESTIAL • CIENCIA • COLOR • COLOREADA • CUERPO CELESTE • DIBUJO • EDAD MEDIA • ESFERA CELESTE • FAMOSO • GRABADO EN MADERA • HISTORIA • HISTORICO • HOROSCOPO • HYGINUS • ILUSTRACION • IMPORTANTE • MEDIEVAL • MEJORA • MEJORAR • OBRA DE ARTE • PLANCHA DE MADERA • S. -XV • SIGNOS DEL ZODIACO • XILOGRAFIA • ZODIACO
 Pinterest
Pinterest Twitter
Twitter Facebook
Facebook Copiar enlace
Copiar enlace Email
Email
