alb3819365
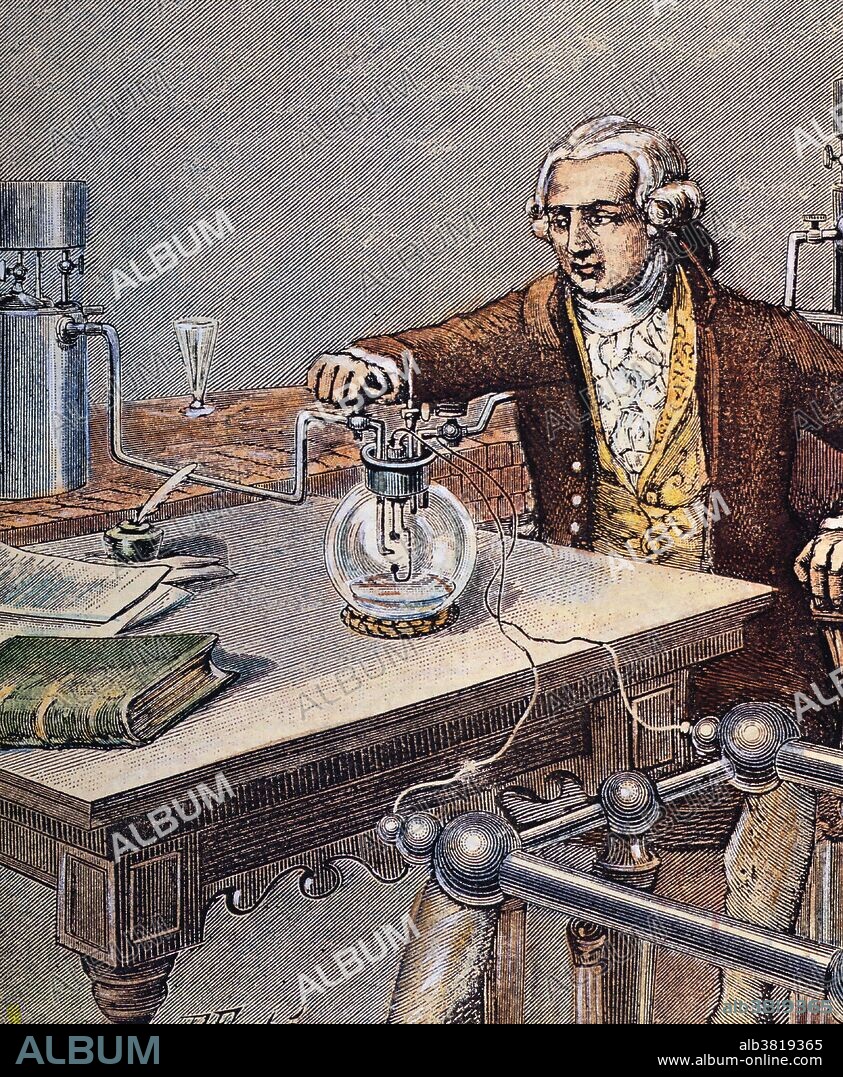
Antoine-Laurent Lavoisier, French Chemist
|
Añadir a otro lightbox |
|
Añadir a otro lightbox |



¿Ya tienes cuenta? Iniciar sesión
¿No tienes cuenta? Regístrate
Compra esta imagen

Título:
Antoine-Laurent Lavoisier, French Chemist
Descripción:
Ver traducción automática
Lavoisier in his laboratory. Antoine-Laurent Lavoisier (August 26, 1743 - May 8, 1794) was a French chemist who is considered the founder of modern chemistry for changing the science from a qualitative to a quantitative one. He recognized and named oxygen and hydrogen, and opposed the phlogiston theory. He helped construct the metric system, wrote the first extensive list of elements, and helped to reform chemical nomenclature. He was the first to establish that sulfur was an element (1777) rather than a compound. He discovered that, although matter may change its form or shape, its mass always remains the same. His book Methods of Chemical Nomenclature of 1787 set the method of naming substances by their composition of elements, which is still used today. He was branded a traitor by the Convention under Maximilien de Robespierre during the Reign of Terror. He was tried, convicted, and guillotined on May 8, 1794, at the age of 50. A year and a half after his death, Lavoisier was exonerated by the French government. When his private belongings were delivered to his widow, a brief note was included, reading "To the widow of Lavoisier, who was falsely convicted".
Crédito:
Album / NYPL/Science Source
Autorizaciones:
Modelo: No - Propiedad: No
¿Preguntas relacionadas con los derechos?
¿Preguntas relacionadas con los derechos?
Tamaño imagen:
3812 x 4632 px | 50.5 MB
Tamaño impresión:
32.3 x 39.2 cm | 12.7 x 15.4 in (300 dpi)
Palabras clave:
1743 • 1794 • ANTOINE LAURENT DE LAVOISIER • ARTE • CIENCIA • DIBUJO • EJECUTADO • ÉLÉMENTS • EUROPEO • FAMOSO • FIGURA • FRANCES • GENTE • HISTORIA • HISTORICO • HOMBRE • HOMBRES • ILUSTRACION • IMPORTANTE • LABORATORIO • LAVOISIER • MASCULINO • METODOLOGIA • OBRA DE ARTE • PERSONA • PERSONALIDAD • PERSONALIDADES • QUIMICA • QUIMICO • RETRATO DE HOMBRE • SIGLO XVIII
 Pinterest
Pinterest Twitter
Twitter Facebook
Facebook Copiar enlace
Copiar enlace Email
Email
