alb3806498
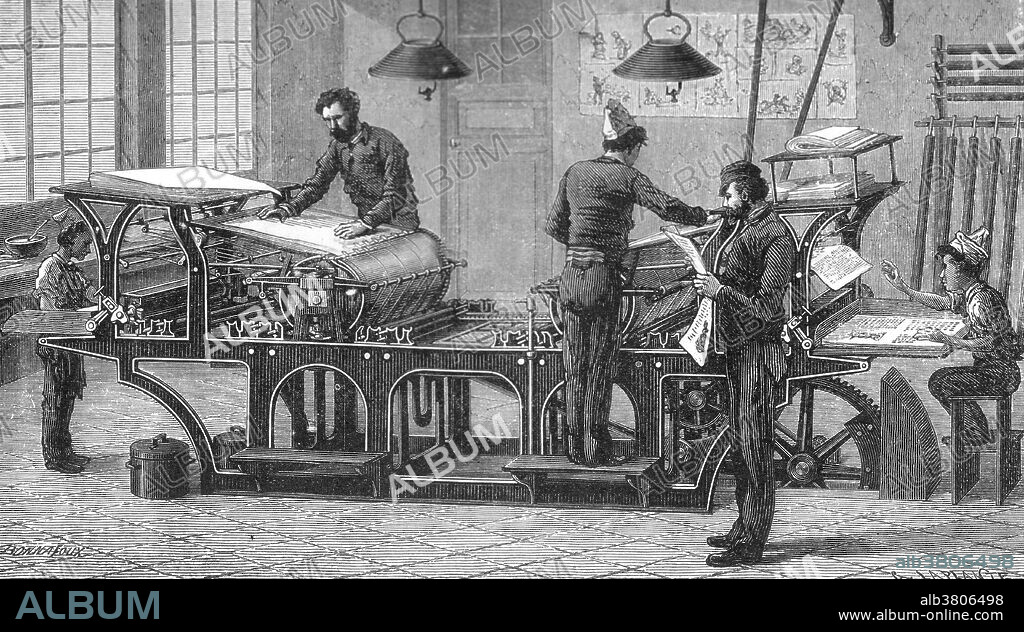
Steam Powered Printing Press, 19th Century
|
Añadir a otro lightbox |
|
Añadir a otro lightbox |



¿Ya tienes cuenta? Iniciar sesión
¿No tienes cuenta? Regístrate
Compra esta imagen.
Selecciona el uso:

Título: Steam Powered Printing Press, 19th Century
Descripción: Ver traducción automática
The steam powered rotary printing press, invented in 1843 in the United States by Richard M. Hoe, allowed millions of copies of a page in a single day. Mass production of printed works flourished after the transition to rolled paper, as continuous feed allowed the presses to run at a much faster pace. A rotary printing press is a printing press in which the images to be printed are curved around a cylinder. Printing can be done on large number of substrates, including paper, cardboard, and plastic. Substrates can be sheet feed or unwound on a continuous roll through the press to be printed and further modified if required.
The steam powered rotary printing press, invented in 1843 in the United States by Richard M. Hoe, allowed millions of copies of a page in a single day. Mass production of printed works flourished after the transition to rolled paper, as continuous feed allowed the presses to run at a much faster pace. A rotary printing press is a printing press in which the images to be printed are curved around a cylinder. Printing can be done on large number of substrates, including paper, cardboard, and plastic. Substrates can be sheet feed or unwound on a continuous roll through the press to be printed and further modified if required.
Crédito: Album / Science Source
Autorizaciones: ? Cesión de modelo: No - ? Cesión de propiedad: No
¿Preguntas relacionadas con los derechos?
¿Preguntas relacionadas con los derechos?
Tamaño imagen: 4800 × 2713 px | 37.3 MB
Tamaño impresión: 40.6 × 23.0 cm | 1889.8 × 1068.1 in (300 dpi)
Palabras clave: ARTE • BLANCO Y NEGRO • CHICOS • CIENCIA • COMUNICACION • DIBUJO • EUROPEA • EUROPEAS • EUROPEO • EUROPEOS • FAMOSA • FAMOSO • FAMOSOS • FLEX • GRABADO • HISTORIA • HISTORICO • HOMBRE • HOMBRES • ILUSTRACION • ILUSTRACIONES • IMPORTANTE • INVENCION • MASCULINO • NINO • NINOS • NIÑO • OBRA DE ARTE • OBRADOR • RETRATO DE HOMBRE • SIGLO XIX • TALLER • TECNOLOGÍA • TECNOLÓGICA • VAPOR • WORKSHOP


 Pinterest
Pinterest Twitter
Twitter Facebook
Facebook Copiar enlace
Copiar enlace Email
Email
