alb3795094
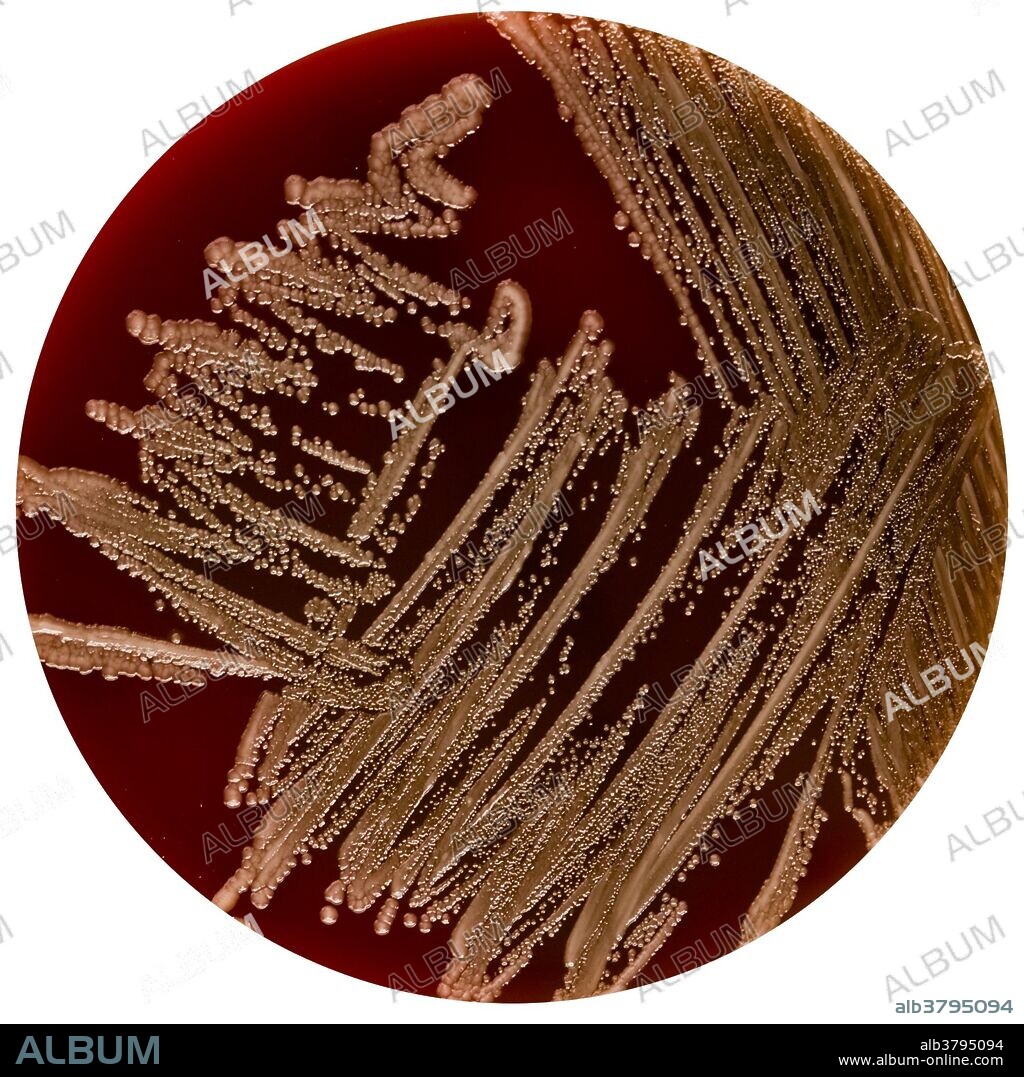
Yersinia Pestis
|
Añadir a otro lightbox |
|
Añadir a otro lightbox |



¿Ya tienes cuenta? Iniciar sesión
¿No tienes cuenta? Regístrate
Compra esta imagen

Título:
Yersinia Pestis
Descripción:
Ver traducción automática
Yersinia pestis (formerly Pasteurella pestis) is a Gram-negative rod-shaped bacterium belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae. It is a facultative anaerobe that can infect humans and other animals. Human Y. pestis infection takes three main forms: pneumonic, septicemic, and the notorious bubonic plagues. All three forms have been responsible for high mortality rates in epidemics throughout human history, including the Black Death (a bubonic plague) that accounted for the death of at least one-third of the European population in 1347 to 1353.
Crédito:
Album / Science Source / Richard J. Green
Autorizaciones:
Modelo: No - Propiedad: No
¿Preguntas relacionadas con los derechos?
¿Preguntas relacionadas con los derechos?
Tamaño imagen:
1750 x 1750 px | 8.8 MB
Tamaño impresión:
14.8 x 14.8 cm | 5.8 x 5.8 in (300 dpi)
Palabras clave:
AGAR • BACTERIA • BACTERIAS • BUBÓNICA • CULTURA • ENTEROBACTERIAS • MICROSCÓPICO • PESTE, LA • PETRI • PLACA DE PETRI • YERSINIA PESTIS • YERSINIA
 Pinterest
Pinterest Twitter
Twitter Facebook
Facebook Copiar enlace
Copiar enlace Email
Email
