alb3776689
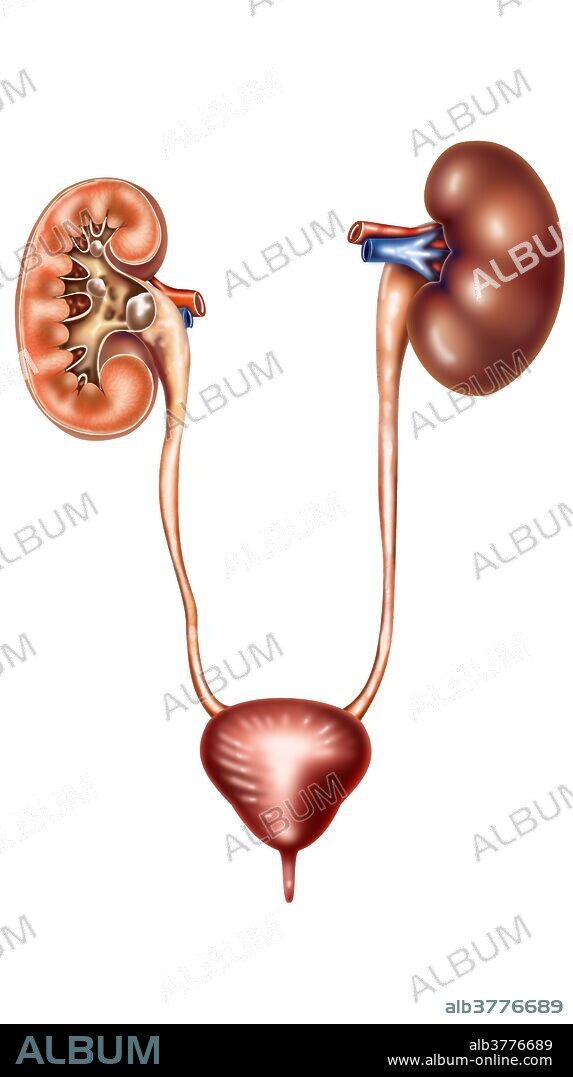
kidney stones
|
Ajouter à une autre Lightbox |
|
Ajouter à une autre Lightbox |



Avez-vous déjà un compte? S'identifier
Vous n'avez pas de compte ? S'inscrire
Acheter cette image

Titre:
kidney stones
Légende:
Voir la traduction automatique
A kidney stone, also known as a renal calculus is a solid concretion or crystal aggregation formed in the kidneys from dietary minerals in the urine. Urinary stones are typically classified by their location in the kidney (nephrolithiasis), ureter (ureterolithiasis), or bladder (cystolithiasis), or by their chemical composition (calcium-containing, struvite, uric acid, or other compounds). Kidney stones typically leave the body by passage in the urine stream, and many stones are formed and passed without causing symptoms. If stones grow to sufficient size they can cause obstruction of the ureter. Ureteral obstruction causes postrenal azotemia and hydronephrosis (distension and dilation of the renal pelvis and calyces), as well as spasm of the ureter. This leads to pain, most commonly felt in the flank (the area between the ribs and hip), lower abdomen and groin (a condition called renal colic). .When a stone causes no symptoms, watchful waiting is a valid option. For symptomatic stones, pain control is usually the first measure, using medications such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or opioids. More severe cases may require surgical intervention. For example, some stones can be shattered into smaller fragments using extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL). Some cases require more invasive forms of surgery. Examples of these are cystoscopic procedures such as laser lithotripsy, or percutaneous techniques such as percutaneous nephrolithotomy. Sometimes, a tube (ureteral stent) may be placed in the ureter to bypass the obstruction and alleviate the symptoms, as well as to prevent ureteral stricture after ureteroscopic stone removal.
Personnalités:
Crédit:
Album / Science Source / Gwen Shockey
Autorisations:
Modèle: Non - Propriété: Non
Questions sur les droits?
Questions sur les droits?
Taille de l'image:
4200 x 7500 px | 90.1 MB
Taille d'impression:
35.6 x 63.5 cm | 14.0 x 25.0 in (300 dpi)
Mots clés:
ANATOMIE • CALCUL RENAL • COUPE TRANSVERSALE • DESORDRE • GRAPHIQUE • HUMAIN • ILLUSTRATION • INSALUBRE • MASS • PARTIE DU CORPS • PERSONNE • URETERE
 Pinterest
Pinterest Twitter
Twitter Facebook
Facebook Copier le lien
Copier le lien Email
Email
